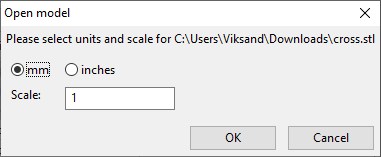
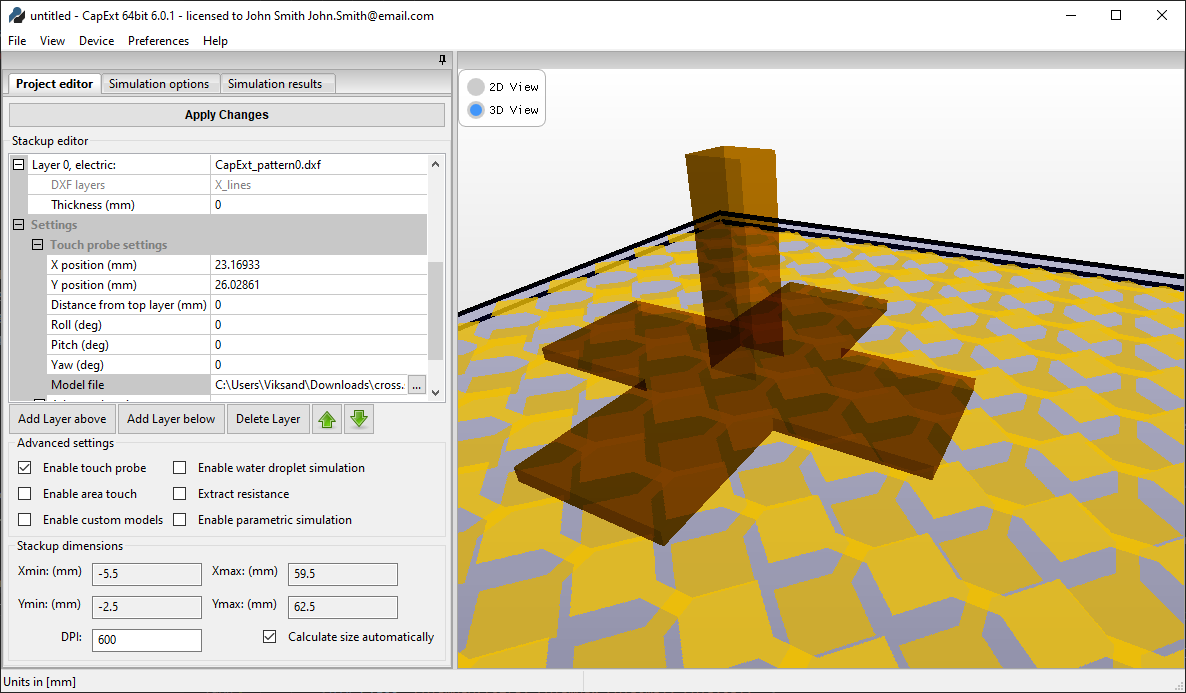
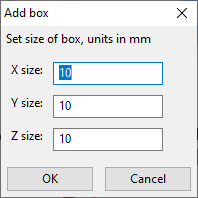
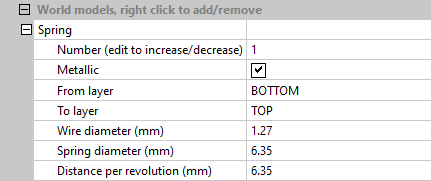
Install license file
If CapExt could not detect a license file, or the previous license has expired, the license manager will be displayed on start-up. If you have a valid license, select "browse" and choose the file.
If you are already running CapExt under a valid license, but want to change the license file, for example to change user or to go from a trial license to a full license, go to About->Open License Manager to open the license manager again.
File support
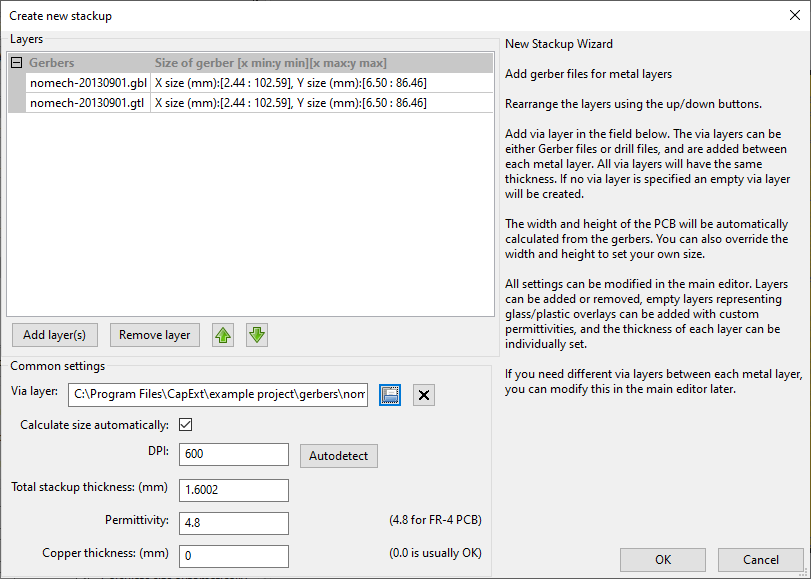
CapExt can import Gerbers, Excellon drill files and DXF-files.
If you want support for other formats, please contact us at info@capext.com
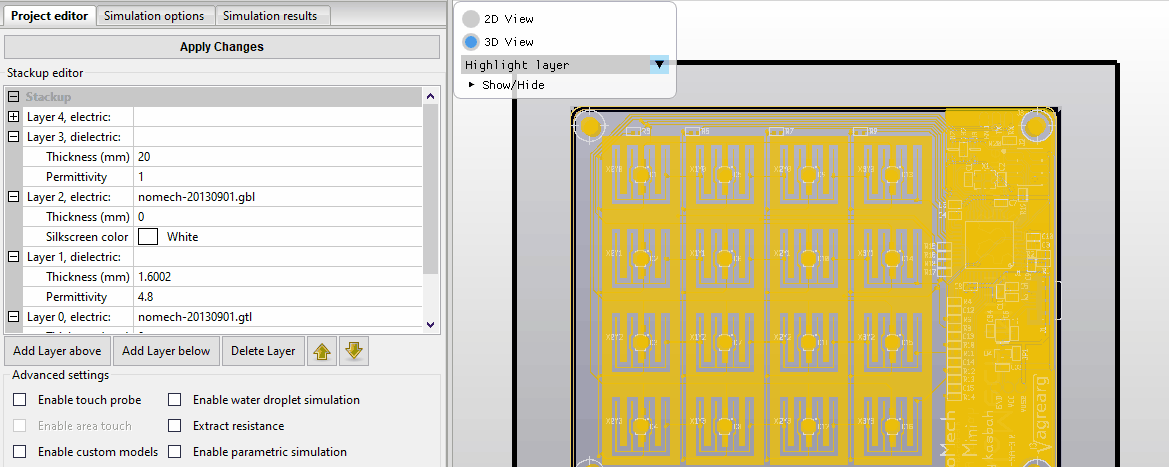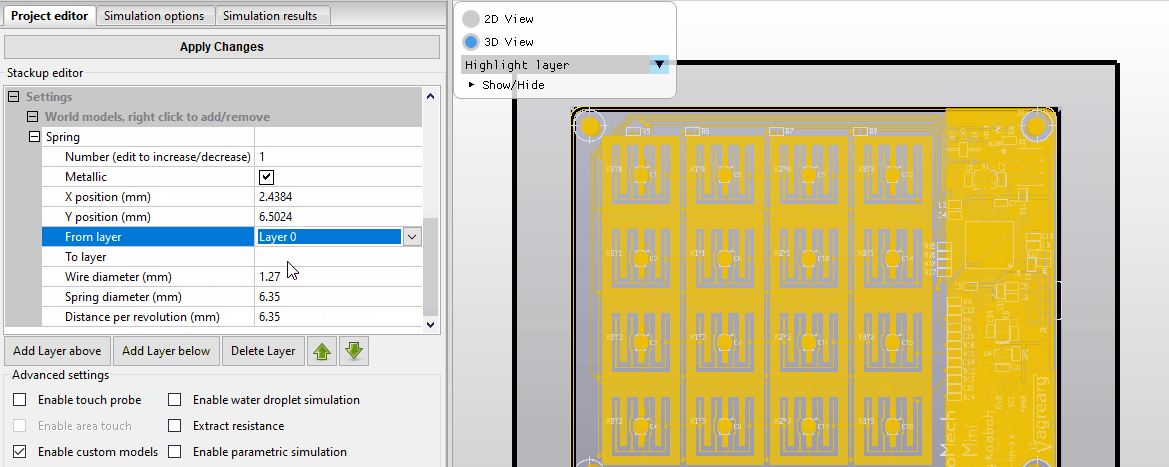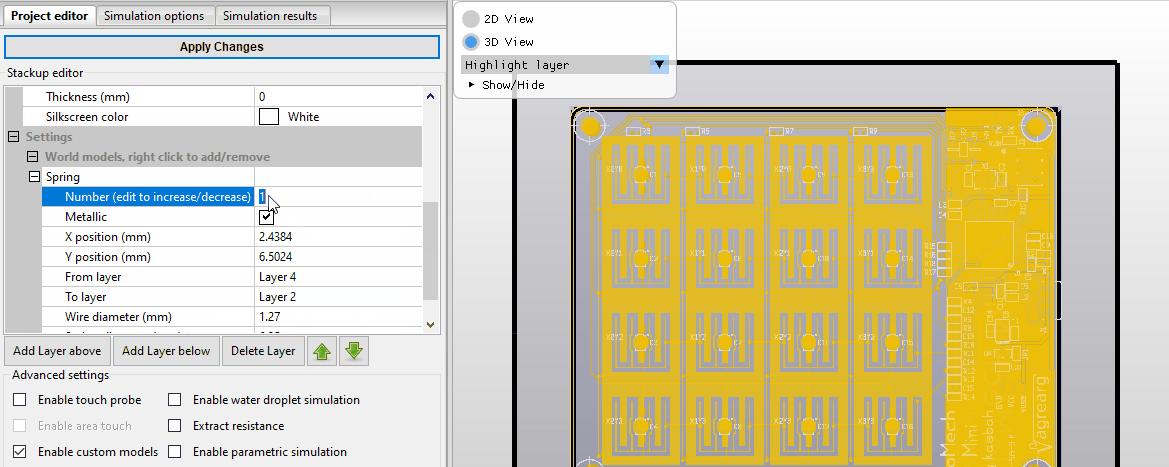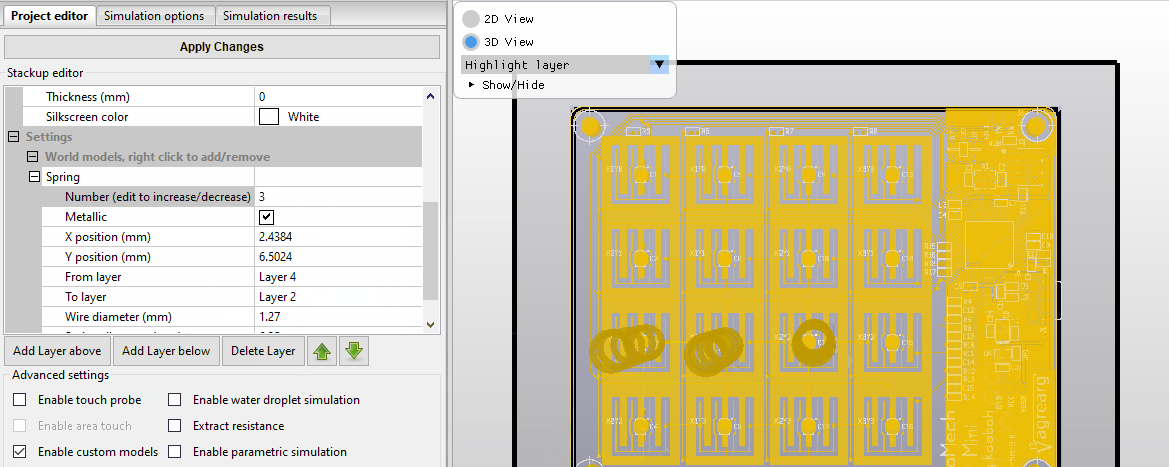
Quickstart examples
CapExt comes with pre-built example projects with matching Gerber files which you can use to quickly familiarize you with how CapExt works, and how to extract the capacitances from your stackup in CapExt. The examples are located in the folder where you installed CapExt, typically C:\Program Files\CapExt\example project\
Back to contents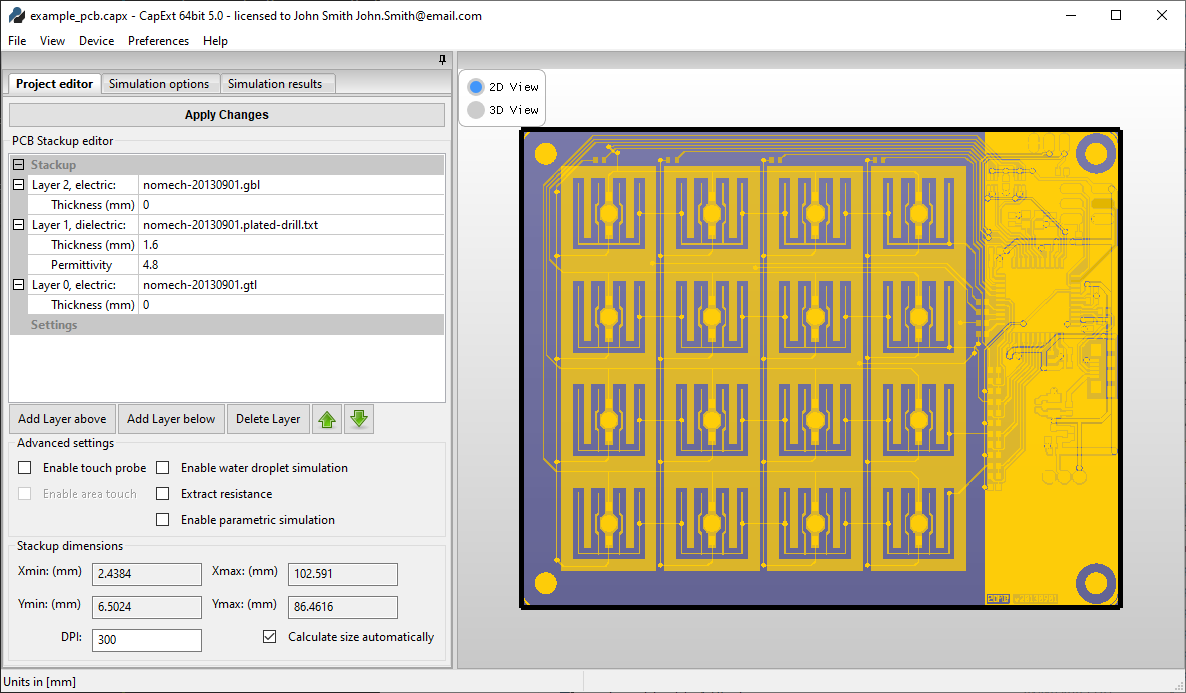 Click
to magnify.
Click
to magnify.
 Click
to magnify.
Click
to magnify.
 Drill file import
wizard
Drill file import
wizard
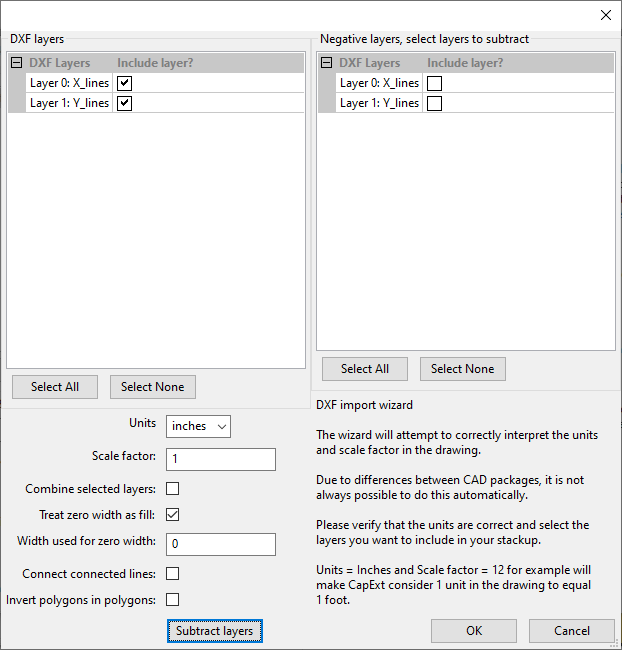 DXF import
wizard
DXF import
wizard
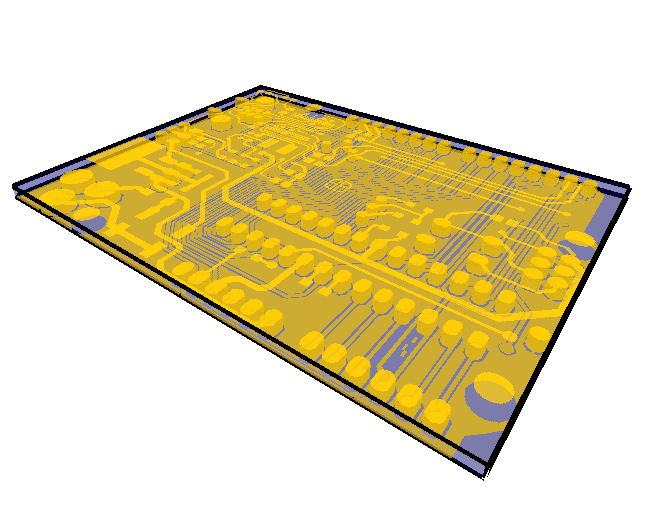 3D view
3D view 2D view
2D view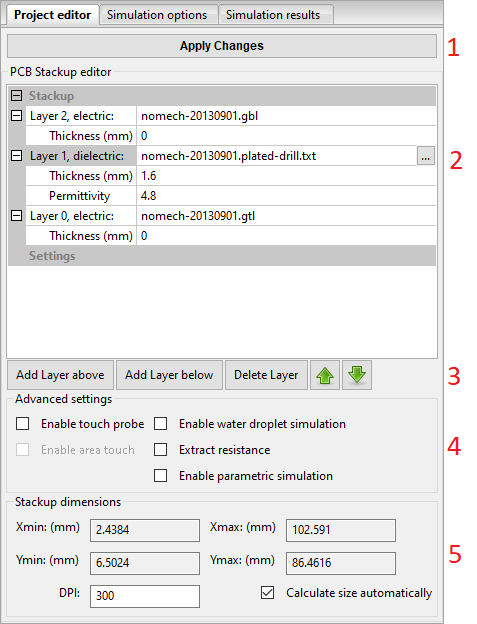 Click
to magnify.
Click
to magnify.

 Click
to magnify.
Click
to magnify.
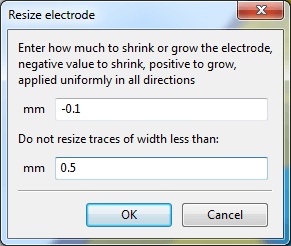
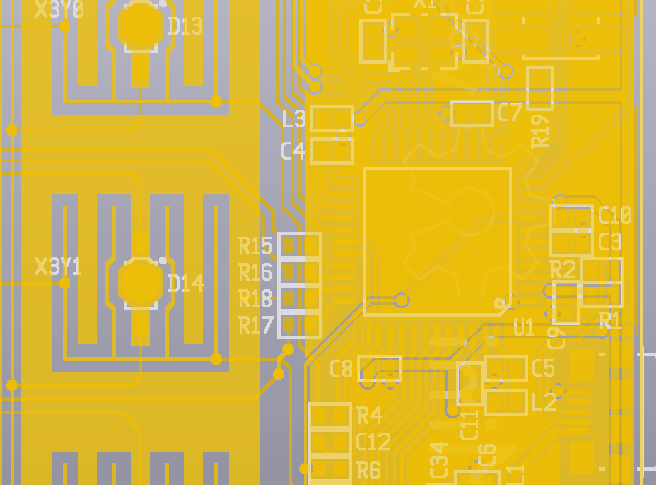
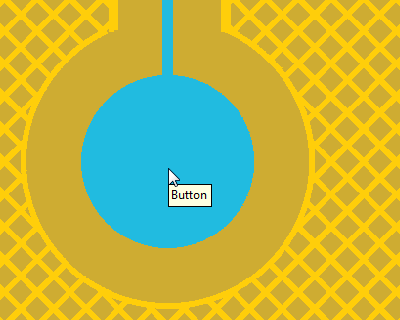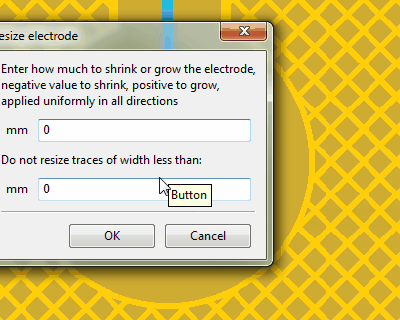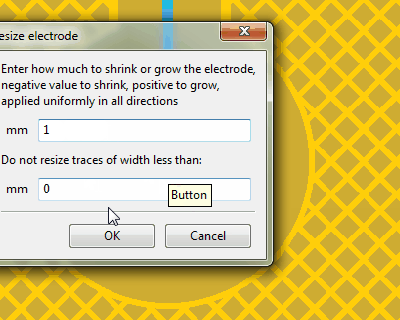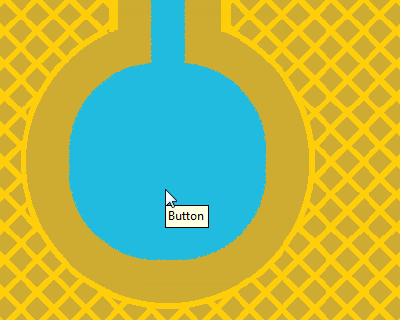
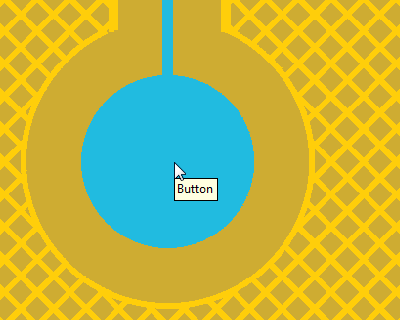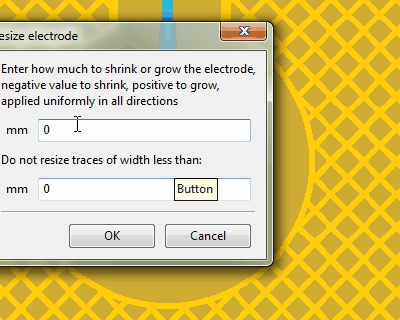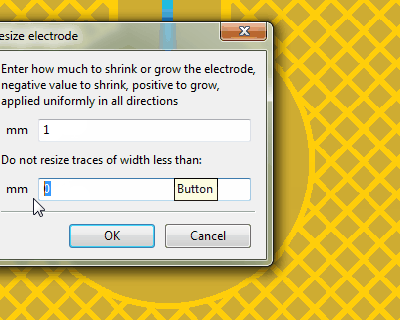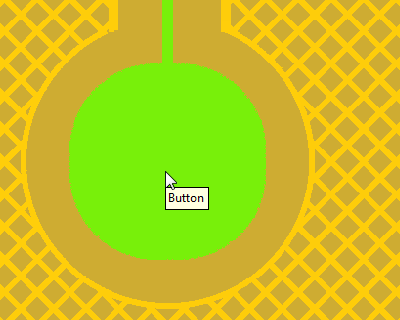
 Using the shrink/grow functionality to reduce the ground hatch
Using the shrink/grow functionality to reduce the ground hatch
 Without trace width set
the trace is also expanded
Without trace width set
the trace is also expanded
 Trace width set to avoid changing trace size
Trace width set to avoid changing trace size
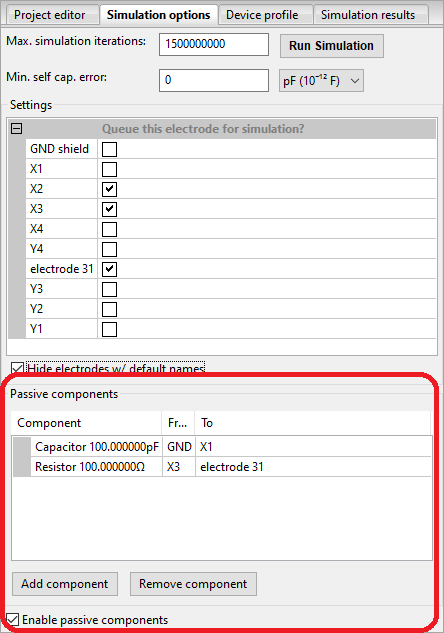 Click
to magnify.
Click
to magnify.
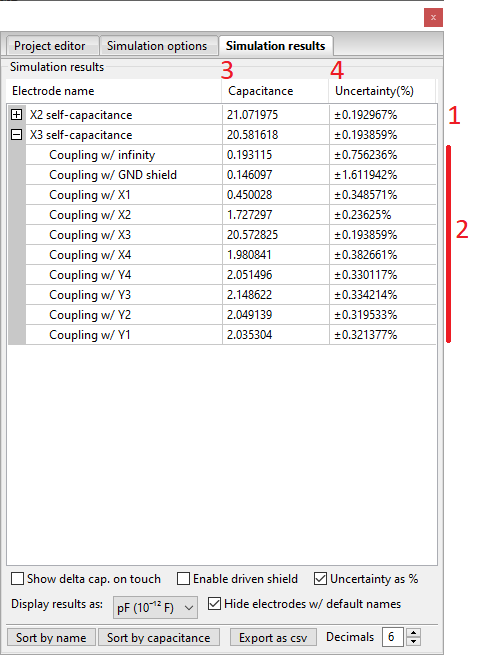 Click
to magnify.
Click
to magnify.
 No driven
shield
No driven
shield
 Bottom
layer
configured as a driven shield
Bottom
layer
configured as a driven shield
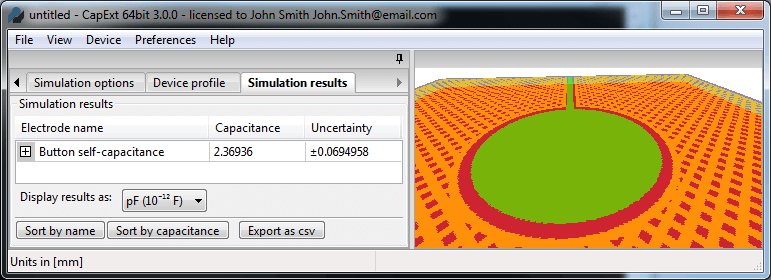
 Click
to magnify.
Click
to magnify.
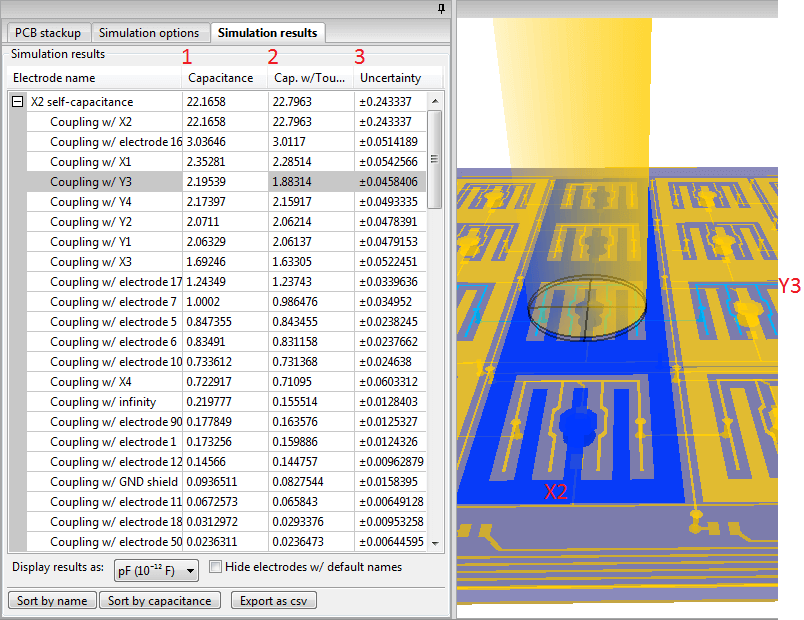 Click
to magnify.
Click
to magnify.

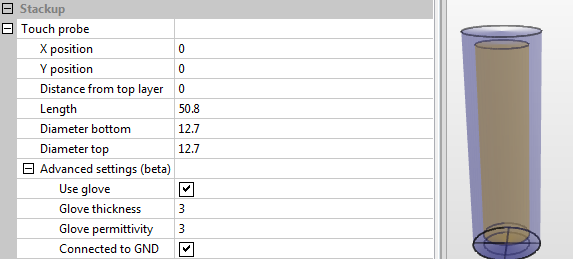 Finger with glove
Finger with glove
 Click
to magnify.
Click
to magnify.
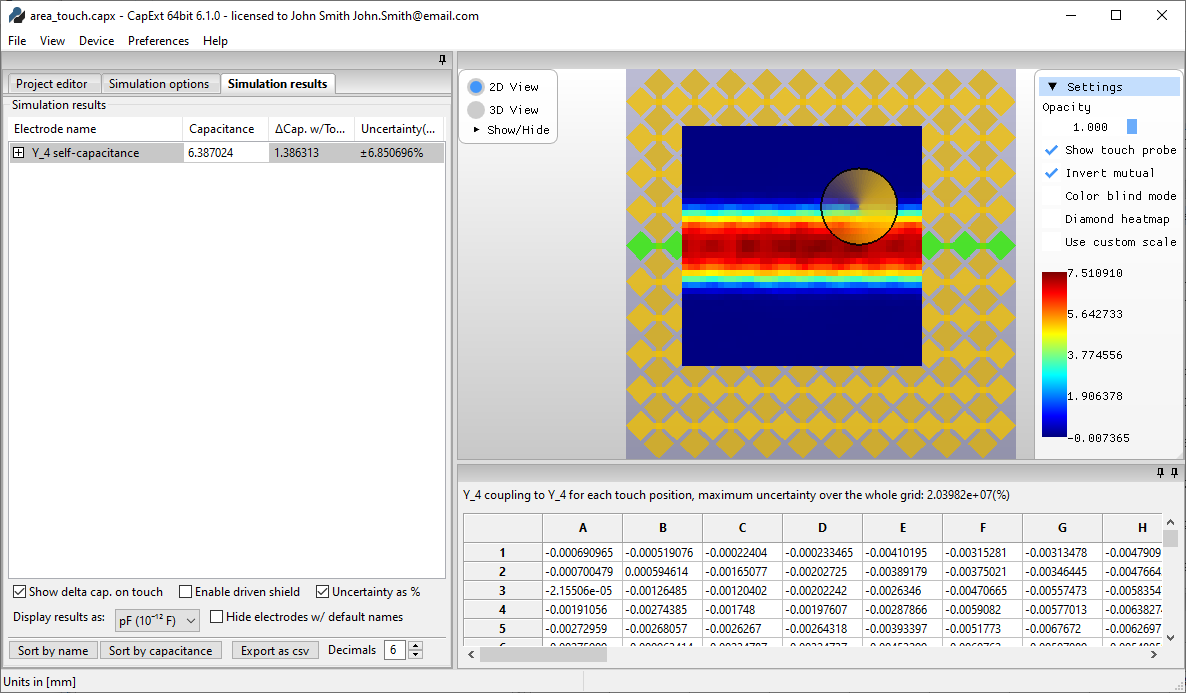 Click
to magnify.
Click
to magnify.
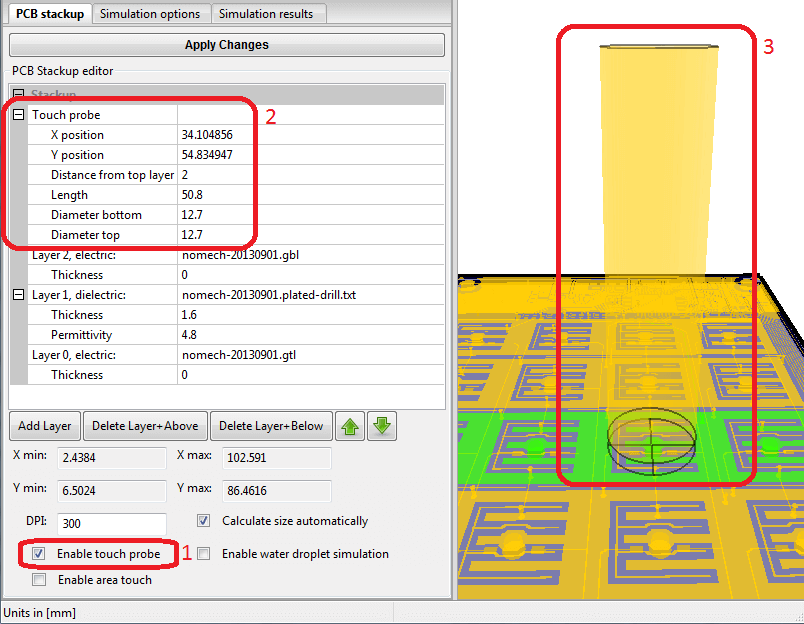
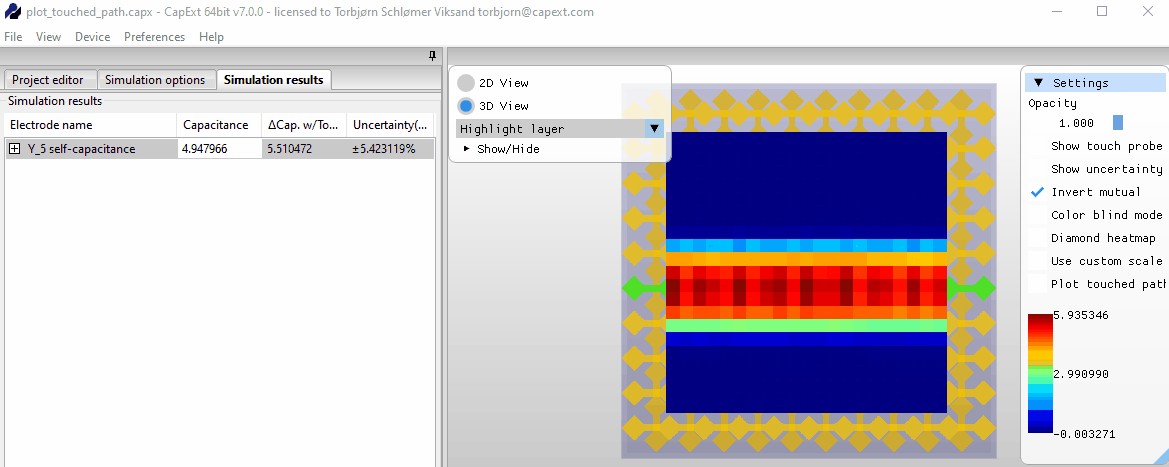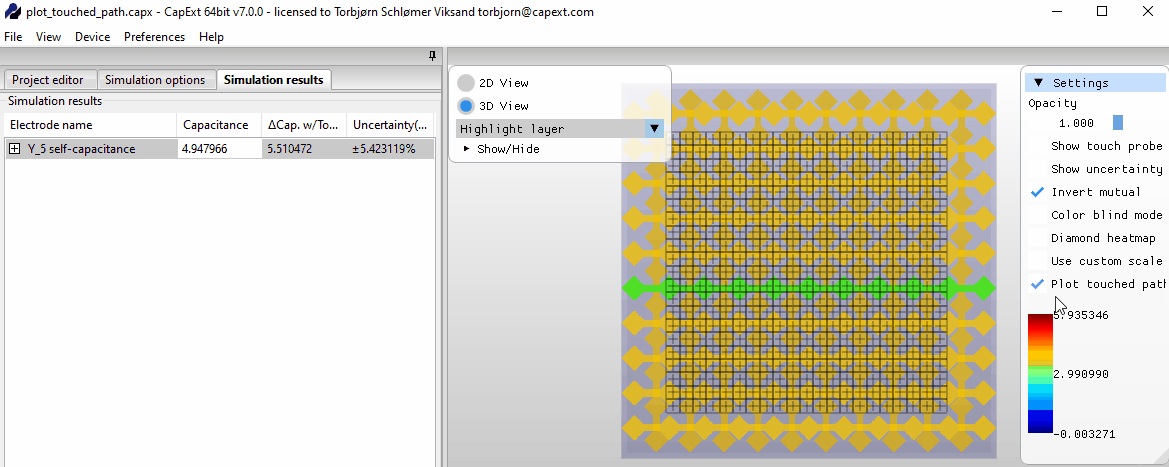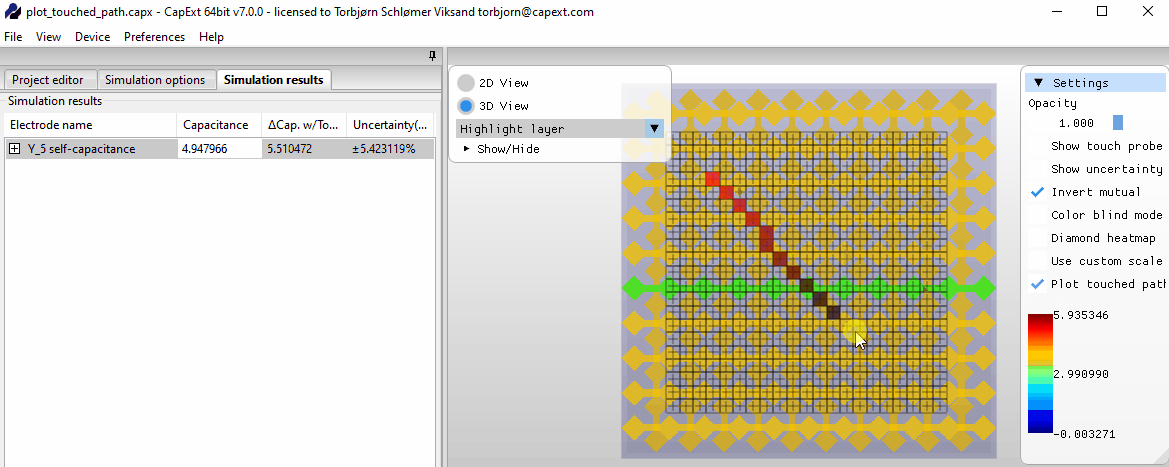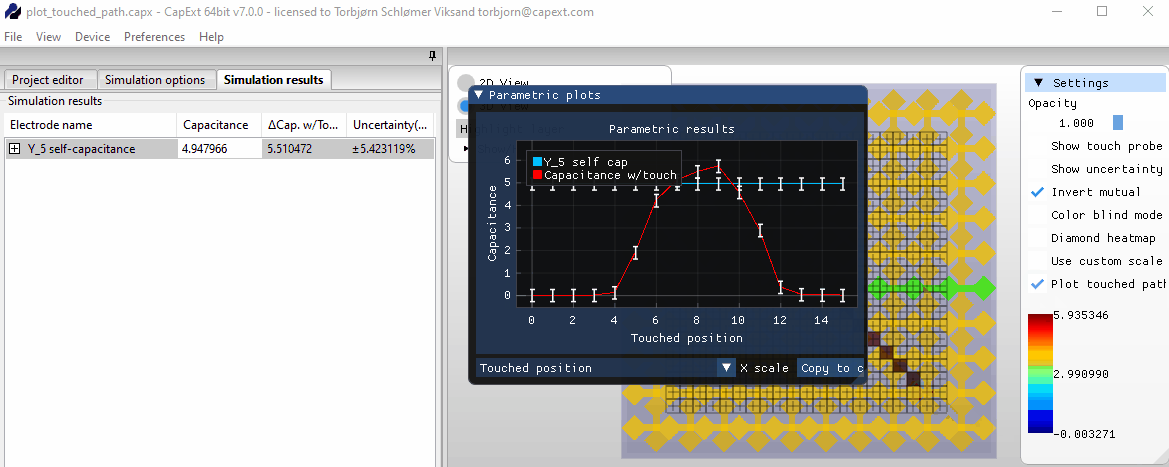
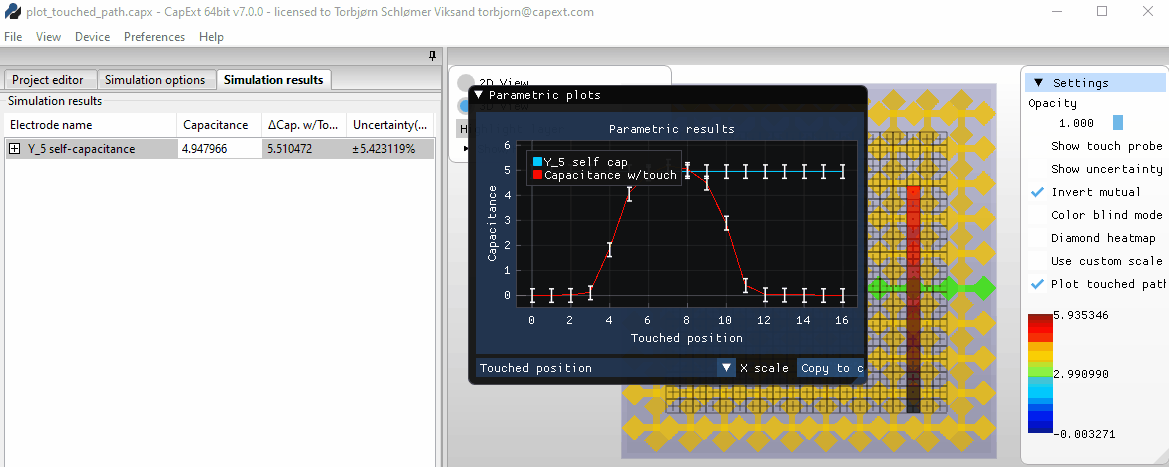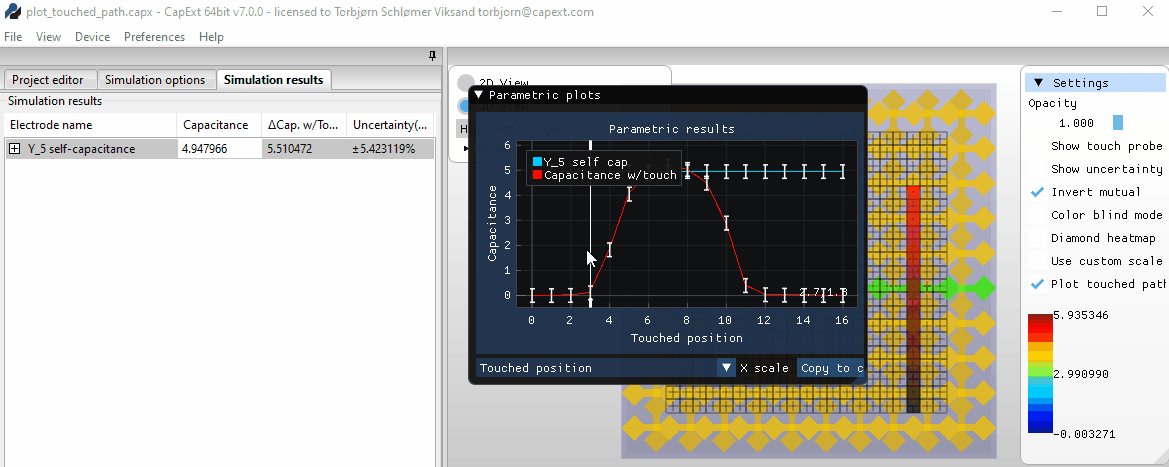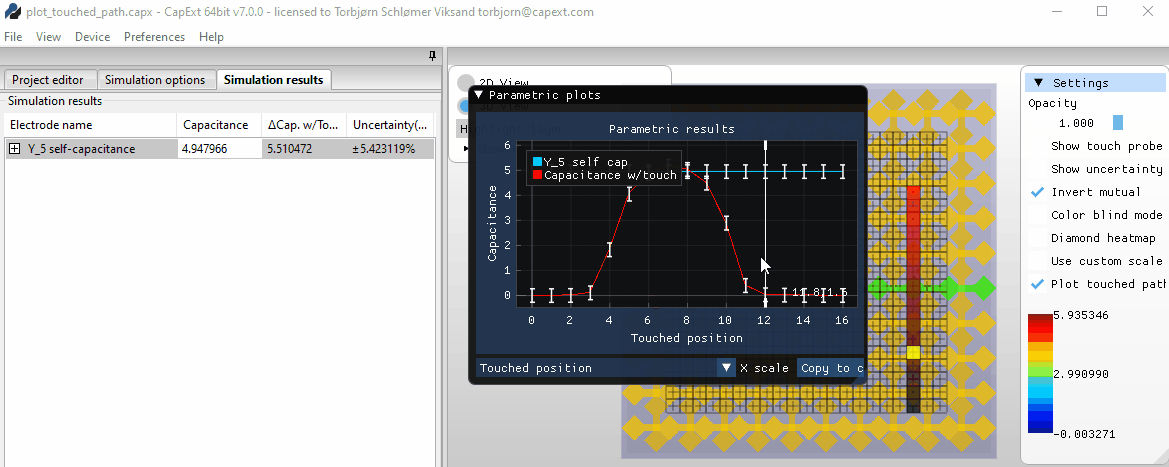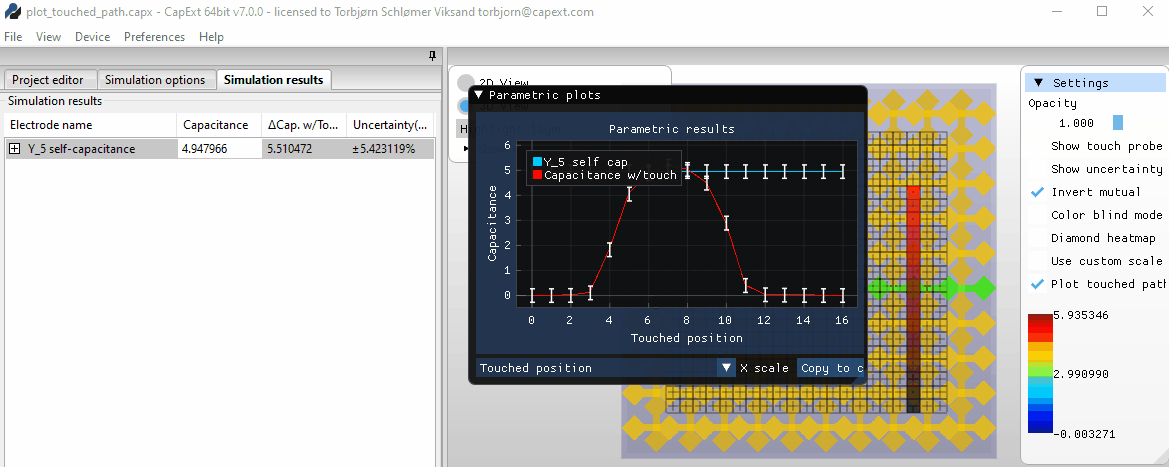
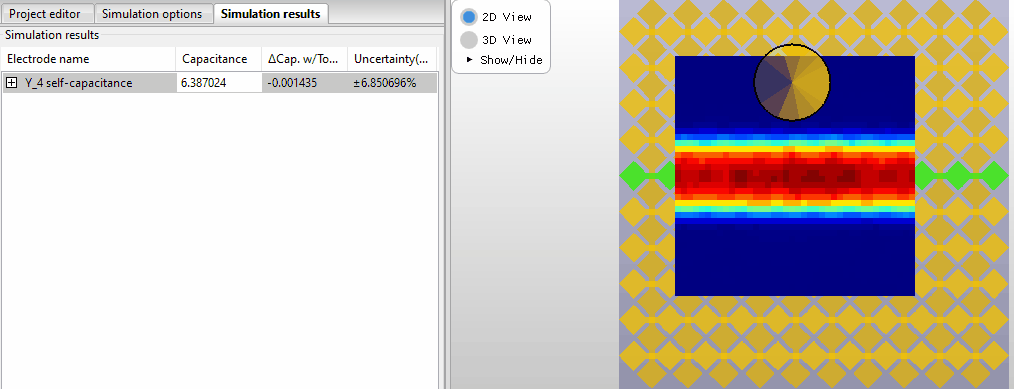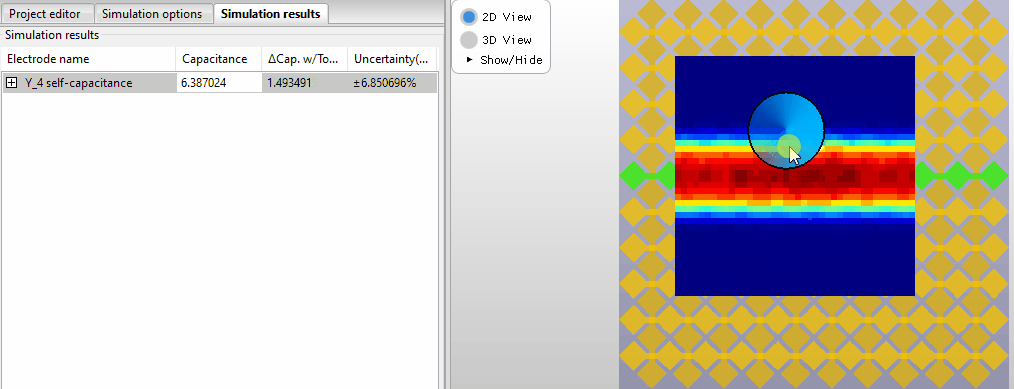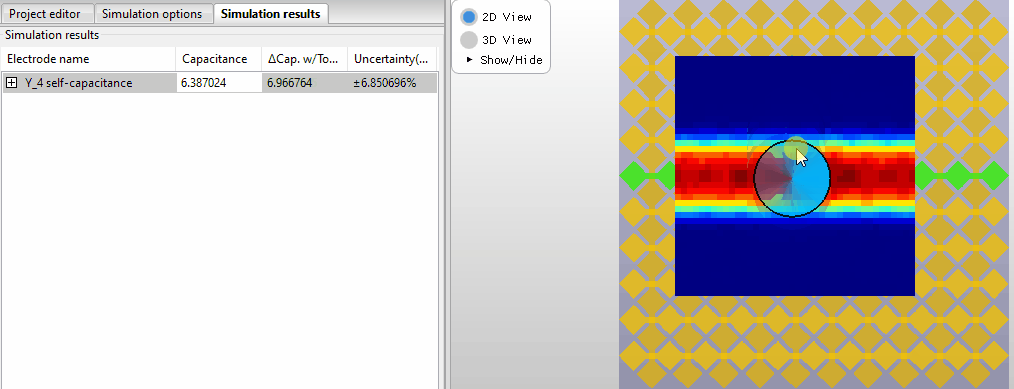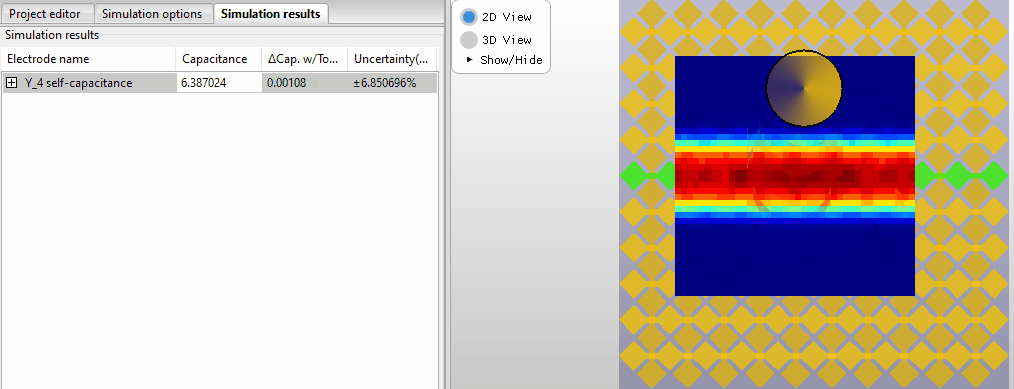 Selecting new probe positions
Selecting new probe positions
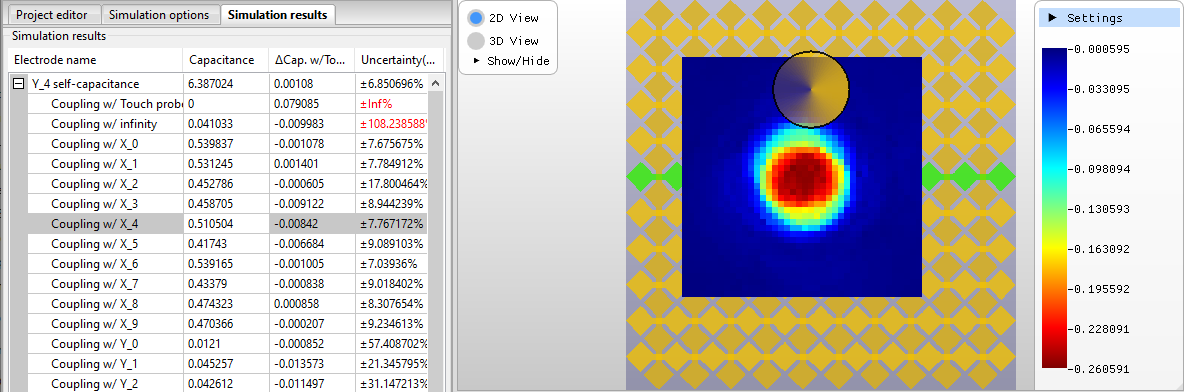 Area
touch and mutual capacitance
Area
touch and mutual capacitance
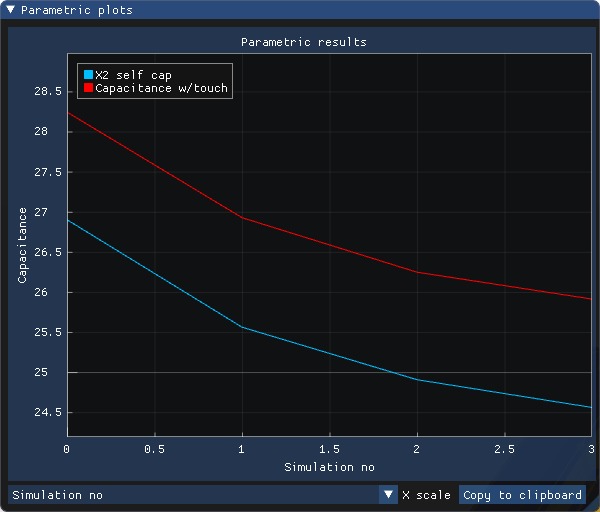
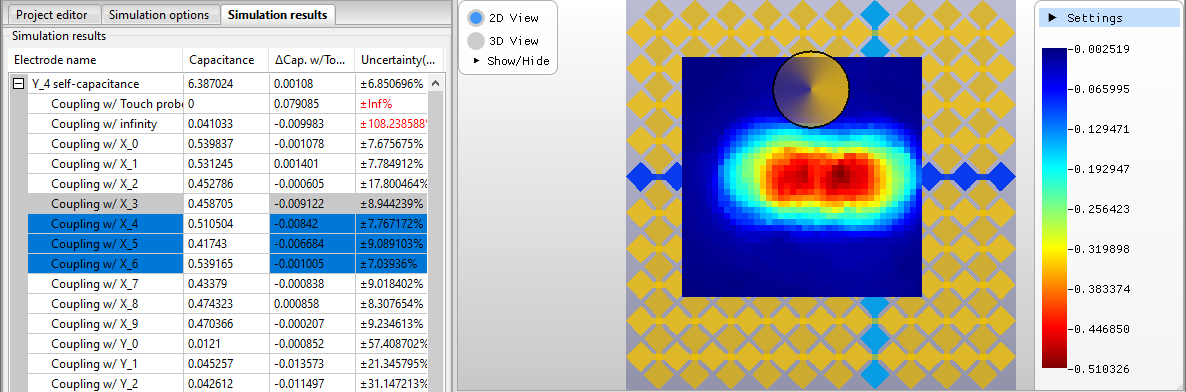 Adding up several mutual capacitances to see linearity
Adding up several mutual capacitances to see linearity
 Configuring
the scale
Configuring
the scale
 Opacity =
0.5
Opacity =
0.5
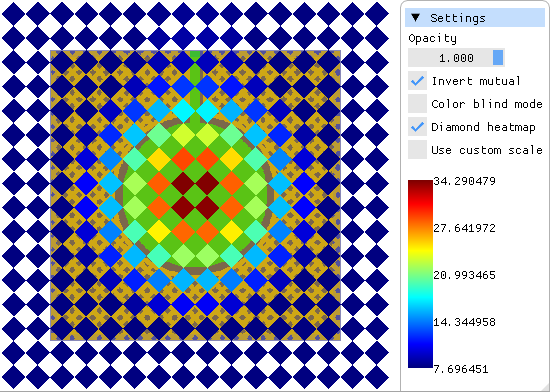 Diamond
heatmap
Diamond
heatmap
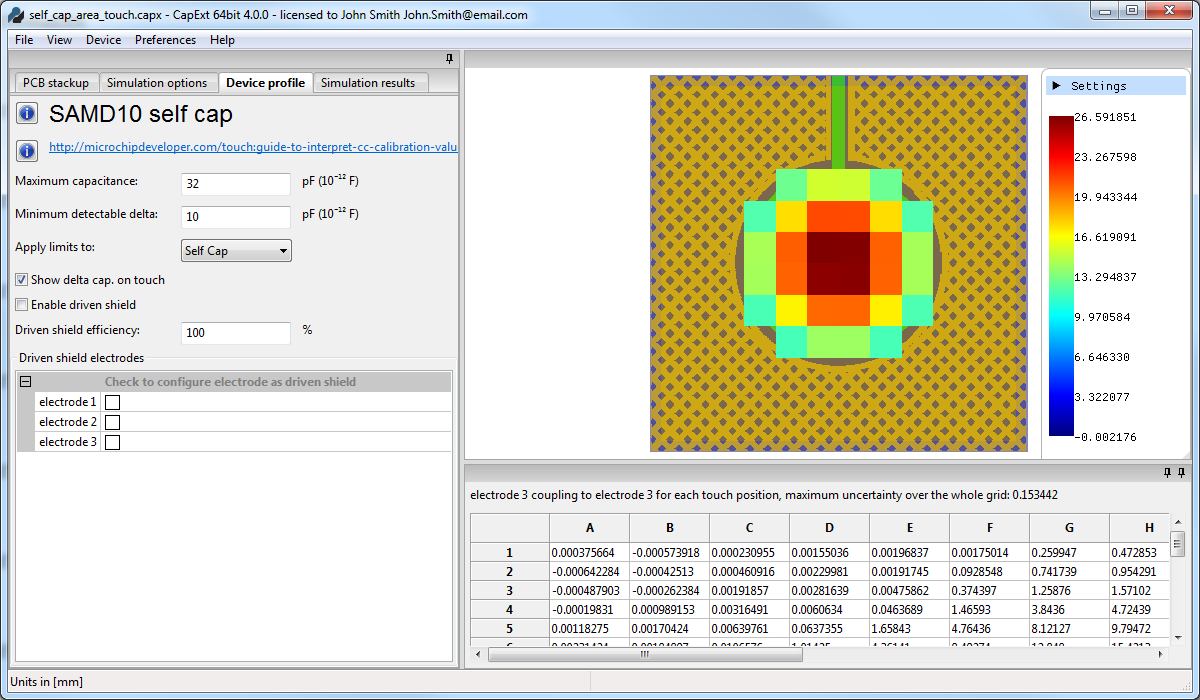 Minimum
detectable
delta tuned to give the optimal touch response
Minimum
detectable
delta tuned to give the optimal touch response

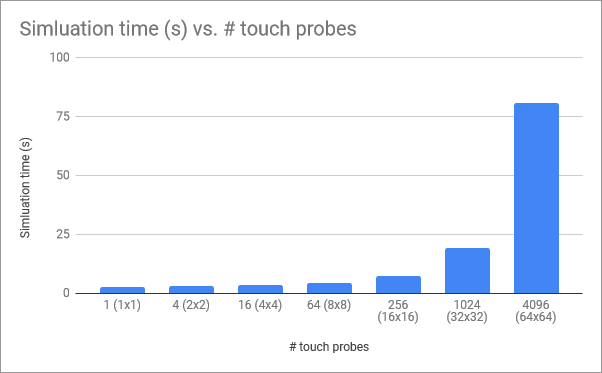 Simulation
time vs # touch probes
Simulation
time vs # touch probes
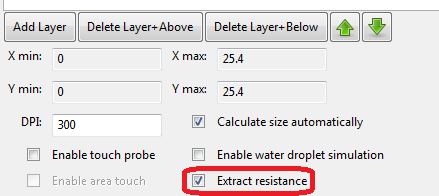
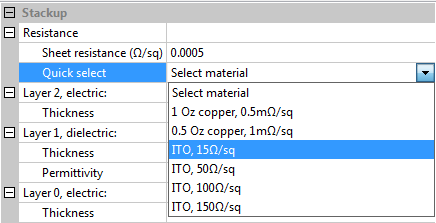
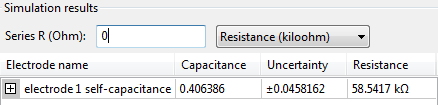

 Click
to magnify.
Click
to magnify.
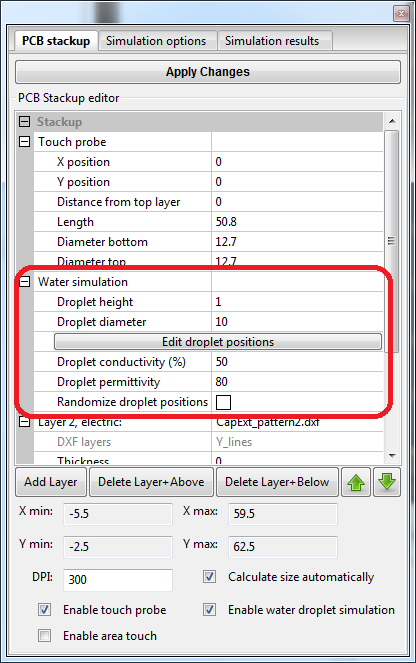 Water simulation
Water simulation
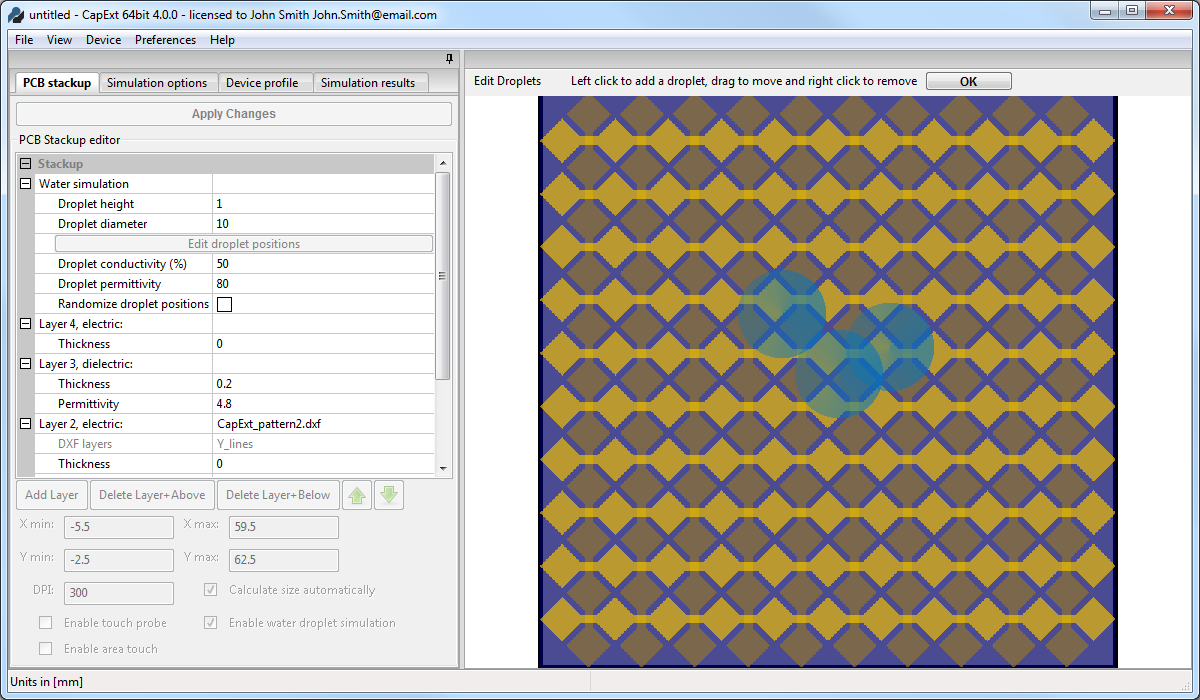 Droplet editor
Droplet editor
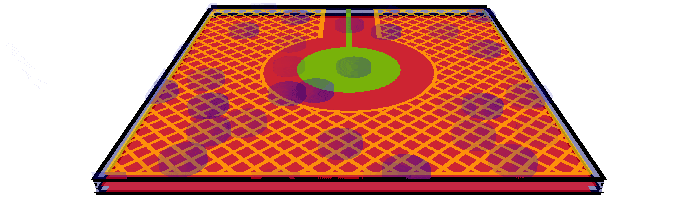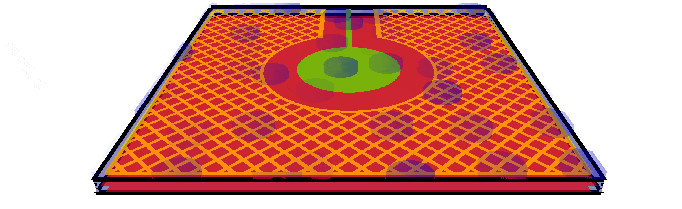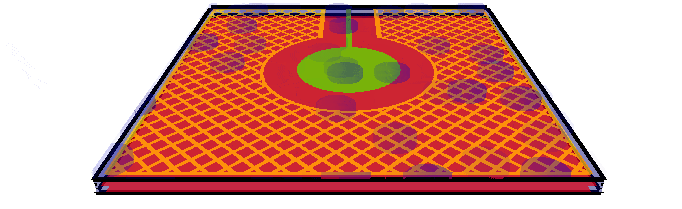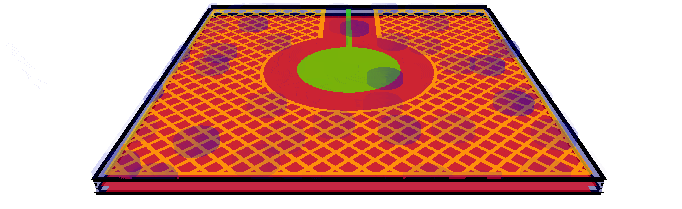 Water
droplets with driven shield
Water
droplets with driven shield
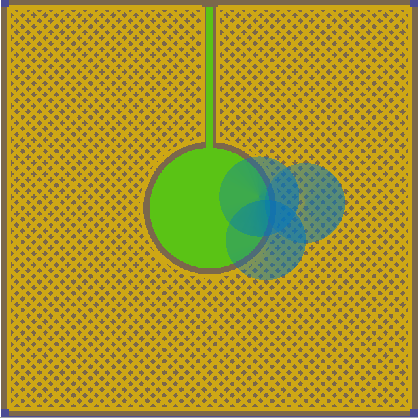 The
droplet pattern used
The
droplet pattern used
 Without
droplets
Without
droplets
 With
droplets
With
droplets
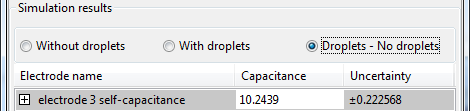 Droplets
- no droplets
Droplets
- no droplets
 Area
touch without droplets
Area
touch without droplets
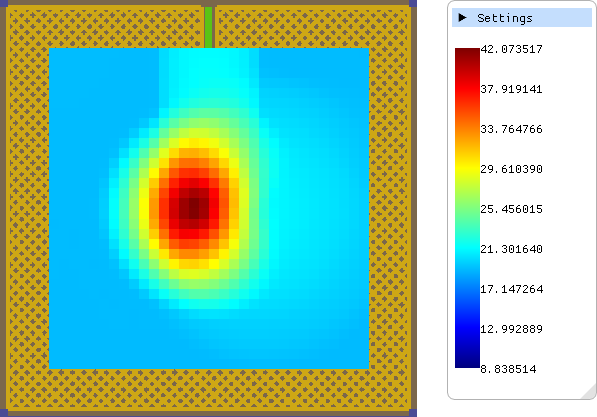 Area
touch
with droplets
Area
touch
with droplets
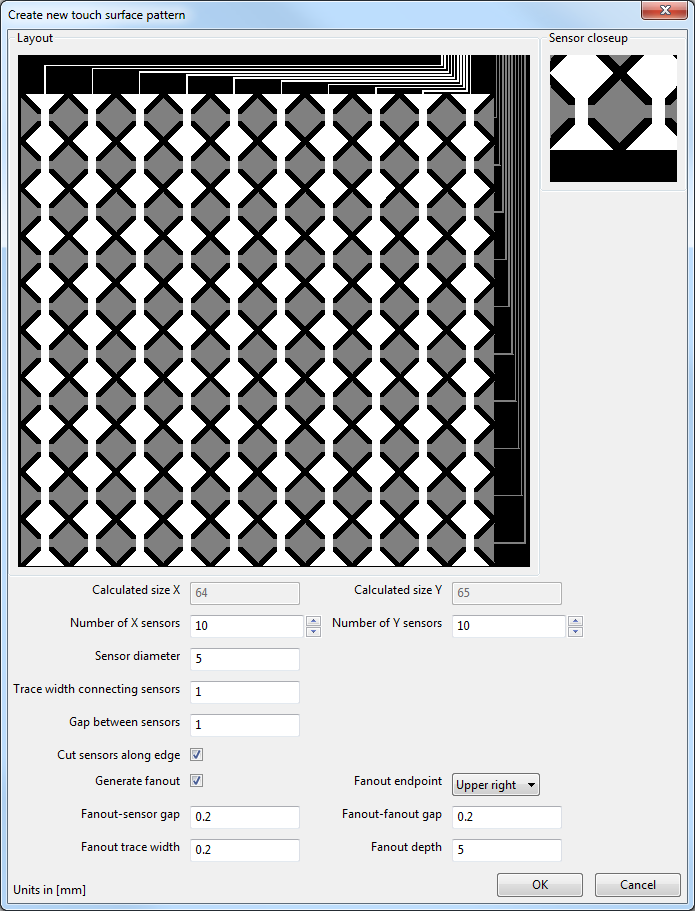 Pattern
generator
Pattern
generator